What is Asbestosis?
Asbestosis is an occupational lung disease caused by asbestos exposure. Asbestos is a material used in many homes and businesses to prevent fire, but it can be dangerous when fibers are released into the air. Not everyone who breathes in these particles will develop asbestosis, which makes it difficult to protect workers against this illness.
An estimated 90,000 people die from asbestosis each year globally according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
What are the symptoms of Asbestosis?
The most common symptom is a chronic cough that doesn’t go away. This can be accompanied by shortness of breath, fatigue, and a feeling of tightness in the throat or chest. Other symptoms include:
- A tight feeling in your chest
- Wheezing
- Loss of appetite
- Pain when you breathe deeply or cough
- In rare cases, asbestosis can cause blood clots to form in the lungs or holes to develop between the layers of tissue that line your lungs.
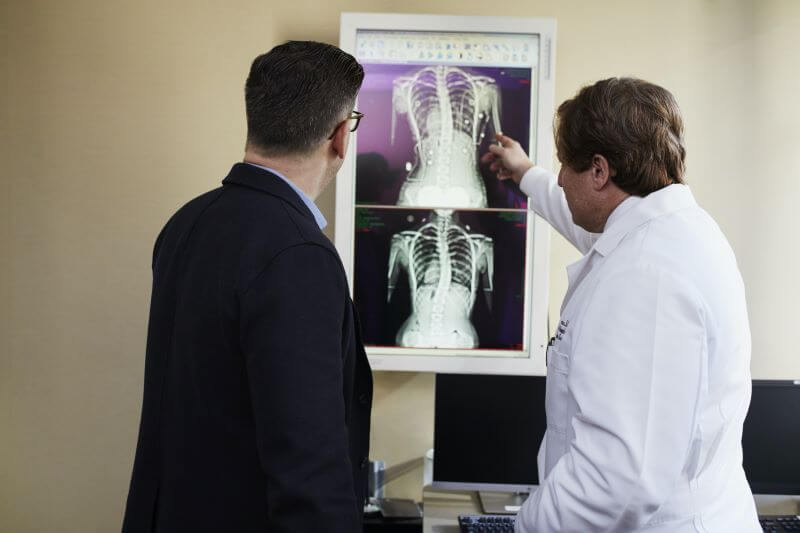
How is Asbestosis diagnosed?
If you have any of the above symptoms, your doctor will order a chest X-ray. During this procedure, your doctor places an instrument on one side of your chest and takes a picture. This shows the bones in your body as well as the outline of your lungs. If abnormalities are found during the X-ray or if they find signs of other lung problems, they will conduct more tests to diagnose asbestosis.
These tests include:
- A computerized tomography (CT) scan
- Pulmonary function tests that measure how well your lungs are working
- Measuring carbon monoxide gas in the air exhaled by the lungs (called carbon monoxide diffusing capacity)
- A blood test to rule out other causes for the symptoms
Your doctor will also make a record of your occupational and medical history to calculation the chances you have of developing asbestosis.
CLICK BELOW TO START YOUR FREE ASBESTOS AWARENESS TRAINING DEMO TODAY!
What asbestosis treatments are available?
At the moment, there is no medication that will cure asbestosis. Treatments are mainly focused on managing symptoms and slowing down lung function deterioration.
- Pain medicine can be used to ease discomfort caused by breathing issues
- Some patients may benefit from antibiotics if they have trouble breathing due to fluid in their lungs
- Oxygen therapy: Many patients with moderate or severe cases of asbestosis find it difficult to breathe so they need supplemental oxygen for relief. It makes it easier to move around and reduces fatigue
- Your doctor also might recommend chest physiotherapy to help you cough up mucus more effectively. This will prevent further accumulation of mucus in your lungs which could cause respiratory infections or pneumothorax (a collapsed lung).
- Medication might also be prescribed to ease breathing, reduce inflammation and prevent infections.
- Some patients with severe asbestosis may benefit from surgery. This will remove the inflamed areas of the lungs that cause breathing problems. Alternatively, in some rare cases, a lung transplant may be recommended. However, this is not a common treatment since there are other less invasive remedies available.
Conclusion
Although there currently isn’t any medication developed specifically for treating asbestosis, the chance of developing this condition can decrease if you take measures to protect yourself against asbestos exposure. Worker protection standards exist in most countries but enforcement is not always adequate so it’s up to individuals to avoid high-risk work environments or materials. If you’re worried about your risk, ask your doctor to check if you have any signs of the condition.
Looking For Asbestos Awareness Training Online?
Haztrainer is dedicated to providing OSHA certified training for Asbestos Awareness and Lead Awareness totally online! Our training video courses are fast, efficient, and easy to use. After you complete the training videos you can simply print out your certificate. We are now offering sample training videos for free so you can see first hand how great Haztrainer is before you commit to purchasing the entire course.


Recent Comments